Describe How Meiosis Contributes to Genetic Variation
Describe differences in the effect of increasing the concentration of. During prophase of meiosis I the double-chromatid homologous pairs of chromosomes cross over with each other and often exchange chromosome segments.

Genetic Variation In Meiosis Biology For Majors I
Meiosis is cell division specific to sex cells and involves more than the simple copying of genetic material that occurs during mitosis.
. How do meiosis contributes to genetic variation while mitosis does not. Which events contribute to. Genetic recombination is vital for the existence of genetic variability within a species.
Which result in genetic variation. Phases of meiosis II. Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA.
Each daughter cell created is genetically half-identical to that of its parent cell yet distinctly different from its parent cell and other daughter cells. Meiosis and fertilization create genetic variation by making new combinations of gene variants alleles. Assess how meiosis contributes to genetic variation while mitosis does not.
Mitosis divides once meiosis divides twice. Indpendent assortment of chromosomes. There are three main mechanisms by which genetic variation between individuals in a species may occur.
3 mechanisms contribute to genetic variation. Random mating between organisms. Meiosis is a reduction in cell division.
The G 1 phase which is also called the first gap phase is the first phase of the interphase and is focused on cell growth. Snyapsis occurs in meiosis but not mitosisMitosis produces 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell meiosis produces 4 cells that have genetic variation. IST1H3 EK How meiosis reduces chromosome number by half.
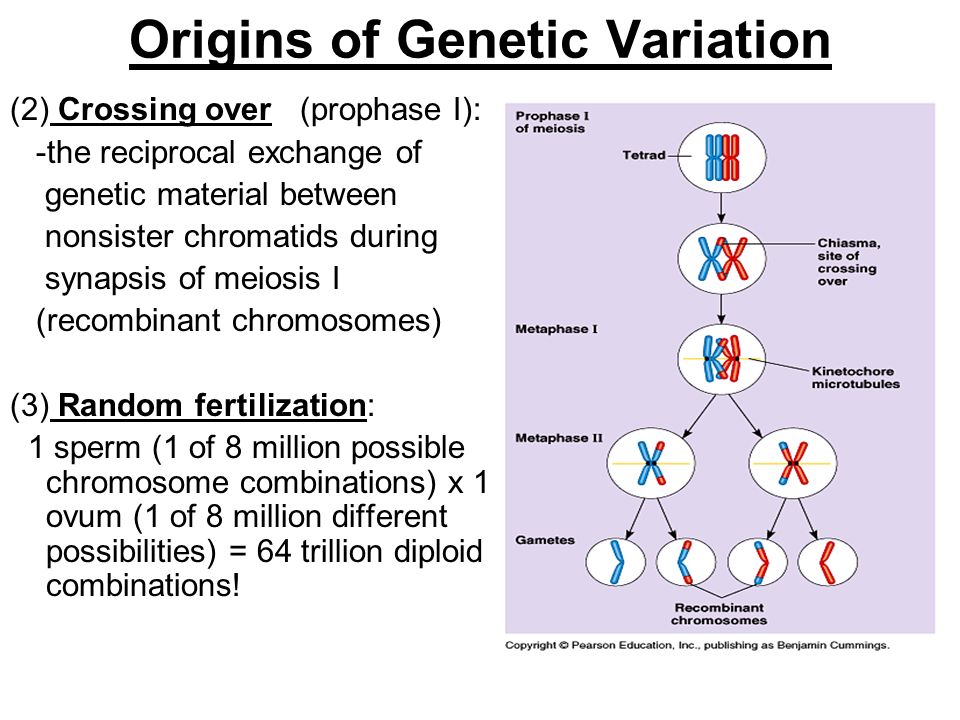
Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA. Meiosis Via either crossing over prophase I or independent assortment metaphase I. What are the three ways meiosis increases genetic variation.
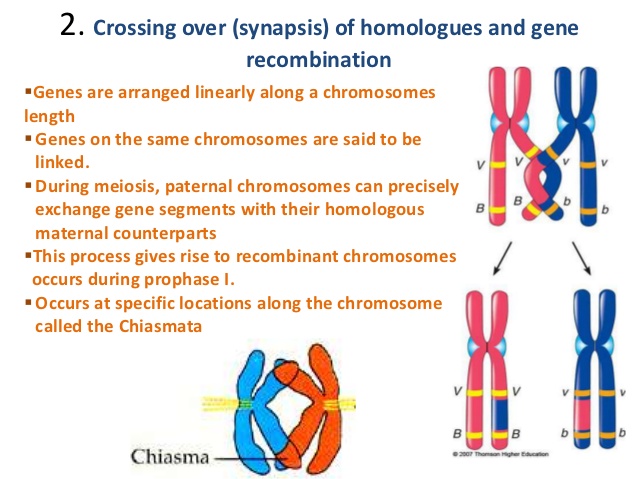
Processes like recombination and crossing over take place during the cell division. During fertilisation 1 gamete from each parent combines to form a zygote. Crossing over or recombination between chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and of nonidentical sister chromatids during meiosis II. Mitosis produces somatic cells meiosis produces gametes. Random fertilization of an ovum by a sperm.
1 identify and describe how meiosis helps contribute and lead to genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms. This recombination creates genetic diversity by allowing genes from each parent to intermix resulting in chromosomes with a different genetic complement. Meiosis contributes to genetic recombination via independent assortment of homologous chromosomes and crossing-over events.
Up to 24 cash back 8describe how meiosis contributes to genetic variation Most variation occurring in each generation relates to how chromosomes behave during meiosis and fertilization. 4 Process Explanation. This recombination creates genetic diversity by allowing genes from each parent to intermix resulting in chromosomes with a different genetic complement.
46 chromosomes produced after mitosis but 23 after meiosis. Mutations Changing the genetic composition of gametes germline mutation leads to changed characteristics in offspring. Crossing over meiosis I meiosis II and genetic variation.
In some cases these new combinations may make an organism more or less fit able to survive and reproduce thus providing the raw material for natural selection. Gametes zygotes haploid diploid. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1 S and G 2 phases which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis.
Mitosis produces identical cells. Phases of meiosis I. Random fertilization of an ovum.
Genetic variation is increased by meiosis During fertilisation 1 gamete from each parent combines to form a zygote. Genomic diversity and genetic variation is produced through the process of meiosis due to chromosomal recombination and independent assortment. Explain how each process contributes to genetic variation.
The three sources of genetic variability in a sexually reproducing organism are. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Variation is geneticvariation and at the cellularDNAlevel-meiosis and mutationare major contributors to variation and so is gene flow.
Start studying Meiosis and Genetic Variation Exam Questions. Click to see full answer. Crossing over of homologous chromosomes.
This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote. Genetic variation is increased by meiosis. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote.
A man produces sperm and a woman produces eggs because their reproductive cells undergo meiosis. Meiosis and genetic diversity. Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes so that gametes are haploid or.
What are 3 reasons to explain genetic variations in meiosis. During meiosis the independent assortment of the pairs of chromosomes and crossing over provide a large amount of genetic variation. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Crossing over between homologous chromosomes during prophase I. How does recombination of genes contribute to genetic variation. Meiosis also creates genetic variation through the process called crossing over where chromosome segments are exchanged.
Both fertilization and meiosis contribute to genetic variation. Meiosis also produces genetic variation by way of the process of recombination. Chromosomal crossover in meiosis I.
The S phase is the second phase of interphase during which the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated.

How Does Meiosis Create Genetic Diversity Socratic

Comments
Post a Comment